LEVEL 2 USER
PayloadPublication (non-standardized parts)¶
Warning
This publication in the version 3 PIM contentmodel is structured according to the version 2 content, mapped to the version 3 methodology, enabling the use of version 3 tooling. However: this publication is NOT an interoperable representation of the version 2 standard. The standard is in the process of revision according to CEN procedures and an update of this Publication is foreseen end of 2018. When these namespaces in this section are used the resulting data exchange is not compliant to any version of the DATEX II standard.
The following namespaces in payloadPublication contain the publications that are structured according to the version 2 informationmodel according to the version 3 methodology.
Each of them contains its specific classes, datatypes and enumerations. Moreover, they gathered their own publications:
- Parking:
- ParkingTablePublication
- ParkingStatusPublication
- ParkingVehiclesPublication
- RoadTrafficData
- ElaboratedDataPublication
- MeasuredDataPublication
- MeasurementSiteTablePublication
- VMS
- VMSpublication
- VmsTablePublication
Each publication must have:
- its creation time “PublicationTime”,
- the language to be used by default,
- a description of the information which is to be found in the publications originating from the particular feed (URL), “FeedDescription”,
- a feed type, which is a classification of the information which is to be found in the publications originating from the particular feed.
- a publication creator which is an international identifier: a two-letter country enumeration (and “other”) plus a national identifier in that country. This creator may be different of the publication supplier.
The following paragraphs detail each publication. The location referencing, which is used by every publication, is detailed in a dedicated paragraph.
Parking¶
Warning
This publication in the version 3 PIM contentmodel is structured according to the version 2 content, mapped to the version 3 methodology, enabling the use of version 3 tooling. However: this publication is NOT an interoperable representation of the version 2 standard. The standard is in the process of revision according to CEN procedures and an update of this Publication is foreseen end of 2018.
ParkingStatusPublication¶
Objectives and utilisation mechanisms
This publication is used to give information on dynamic data of parking sites or groups of parking sites (e.g. free spaces, trends, vehicle count on the parking site …). The publication refers to static information about a parking site or groups of parking sites prior published with the ParkingTablePublication (by using the concept of versioned references).
ParkingTablePublication and ParkingStatusPublication are in accordance with the Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 885/2013 about the provision of information services for safe and secure parking places for trucks and commercial vehicles.
Content
The following topics can be covered by this publication:
- Occupancy information for a parking site, a group of parking sites or a group of parking spaces (all declared in the static model and referenced in this publication):
- Number of spaces (as an override in case of dynamic changes)
- Number of vacant spaces (as a number, as a ‘higher than’ or ‘lower than’ information as well as in an enumerated form)
- Number of occupied spaces (as a number, in enumerated form as well as in trend form)
- Number of parking vehicles
- Information on individual parking spaces (occupied or free, temporary closed)
- Overriding thresholds: It is possible to override the static threshold information, i.e. the defined fill grades of a parking site for which the dynamic status information should change between different states (incl. overcrowding states)
- Status information: A state information on the fill grade of a parking site incl. overcrowding information (in limited form also for a group of parking sites)
- Validity of parking space- and group of parking space-declarations: Spaces might be temporary closed or defined for mixed usage (i.e. declaration not valid all the time).
- Information about the availability of additional equipment or additional service facilities (overriding the amount, current availability, opening and vacancy information).
- Fill- and exit rates (sensor data, which can be based on a static MeasurementSiteTable information)
- Vehicle count within interval, i.e. incoming or outgoing vehicles or change of occupancy within time
By defining the validity of the dynamic information, it is possible to publish real time data, historical data or forecasts. It is also possible to publish series over time.
ParkingTablePublication¶
Objectives and utilisation mechanisms
This publication is used to publish static information of parking sites or groups of parking sites. This comprises urban or interurban parking sites as well as special facility and (secure) truck parking information. It covers on street parking as well as off street parking (car parks, parking places, motorway parking areas …). Within a parking site, information can be specified down to groups of parking spaces or even for individual parking spaces. There are four minor Level B extensions entailed in this publication:
- Area is extended to specify a polygonal area
- Point is extended to specify junctions
- Period is extended to specify special days and holidays
- VehicleCharacteristics is extended to specify additional vehicle types, loads and emission information
The static information forms the base for dynamic occupancy information, for which you should use the ParkingStatusPublication.
ParkingTablePublication and ParkingStatusPublication are in accordance with the Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 885/2013 about the provision of information services for safe and secure parking places for trucks and commercial vehicles.
Content
Because of the size of this publication, it is not described on attribute level here. The description is focussed on included subjects instead:
- For parking sites, groups of parking spaces or individual parking spaces the following assignments can be specified as convenient, as allowed or as not allowed:
- Specified type(s) of users
- Specified type(s) of vehicles (incl. hazardous materials)
- Time (for mixed usage of parking spaces, for example day usage for cars, night usage for lorries).
- Basic information (number of spaces, reservation information, short or long term parking, …), each also possible for individual groups of parking spaces (i.e. for example it is possible to specify the possibility of reservation just for a part of the parking site or to specify the number of parking spaces for lorries).
- Special Permits for users or vehicles (e.g. disabled permit, government permit)
- Permitted or prohibited actions on the parking site (e.g. smoking, camping)
- Contact information (address, telephone number etc.) for the parking site as well as for several other stakeholders or services (e.g. owner, reservation service, …)
- Entrances and exits with characteristics and geo-reference
- Opening times, expressed by the detailed validity model
- Additional equipment and additional service facilities (long list of items, like for example toilets, internet, restaurants, police station) optional each with opening times, tariffs, location, validity or restriction to users or vehicles
- Electric charging stations (incl. technical parameters and connector types)
- Information on the LABEL-categorisation and on security measures
- Tariff information in a complex structure, for different charge bands, depending on user or vehicle type and for different seasons (incl. different types and modes of payment, payment cards and reservation fees)
- Thresholds, i.e. defined fill grades of a parking site for which the dynamic status information should change between different states (incl. overcrowding states)
- Parking Routes incl. geo-reference, direction and colour information
- A colour mapping to occupancy states
- Parking scenario (truck parking, rest area, car sharing, mechanical drop off, …)
- Geo-reference information (all methods which are available in DATEX) for all elements
The following two pictures show information on assignments, dimensions and Geo-referencing, which can be specified with the Parking Table Publication:
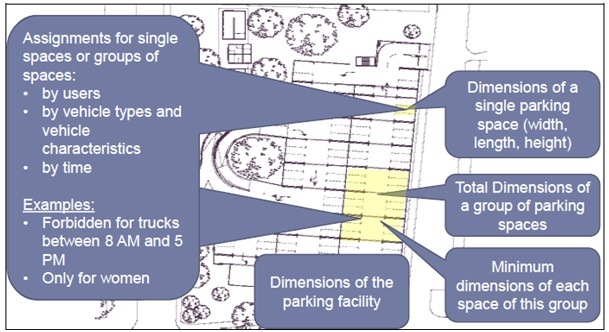
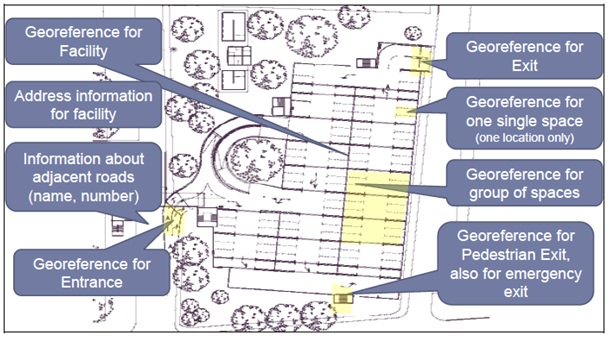
ParkingVehiclesPublication¶
Objectives and utilisation mechanisms
The ParkingVehiclesPublication allows specifying information on specific parking vehicles. The publication refers to static information about a parking site or groups of parking sites prior published with the ParkingTablePublication (by using the concept of versioned references).
Content
For a parking vehicle, the following information can be specified:
- Reference to the parking space used
- The parking period
- The parking permit
- Information about the vehicle, like licence plate information or vehicle characteristics
- Information on the individual charge, including the paid amount or the method of payment
The process of parking must not yet be finished; it is possible to omit the end of the parking period.
RoadTrafficData¶
Warning
This publication in the version 3 PIM contentmodel is structured according to the version 2 content, mapped to the version 3 methodology, enabling the use of version 3 tooling. However: this publication is NOT an interoperable representation of the version 2 standard. The standard is in the process of revision according to CEN procedures and an update of this Publication is foreseen end of 2018.
ElaboratedDataPublication¶
Objectives and utilisation mechanisms
This publication is used to give information that is in some way elaborated or derived. Typically, this is data which has been elaborated by a traffic centre from input data held in its database.
Content
This publication contains one or more elaborated data sets.
With this publication, attributes can be given in the InformationHeader class which provide clients with information management details (area of interest, confidentiality, information status, urgency) relating to this publication.
A set of default values for “forecast”, “period” and “time” can be provided to clients which are applicable throughout the publication if no others are provided at the detailed level. This helps in minimising the size of publications where large numbers of values are sent which share common parameters.
Also to assist in minimising the volume of required values to be sent for traffic status covering wide expanses of a road network, ReferenceSettings can be provided to a client. ReferenceSettings comprise a reference to a predefined set of non-ordered locations (see Predefined Locations publication) and a default value that can be assumed by a client for the traffic status at all these locations if none is received. Thus a supplier only needs to send for those locations the actual values of traffic status which deviate from this default value.
Source information can be given (country, identifier, name, type, reliable) for each elaborated data.
A validity can also be given (as for situation records) composed of:
- An validity status which defines if the record has an “active” status or this status is defined according to periods of time (one can consider the third possible value “suspended” is not applicable for this kind of data element).
- One mandatory global first start time “overallStartTime”
- One optional global real end time “overallEndTime”
- Several periods, each having a start date and an end date, for which the elaborated data is active/valid, detailed with hours/days/weeks/months
- Exception periods, each having a start date and an end date, for which the elaborated data is not active/valid, detailed with hours/days/weeks/months.
The optional “overrunning” is not applicable for this kind of data element.
It can be indicated if the elaborated data is a forecast.
In case of fault when elaborating this data, it is possible to specify the type of fault (intermittent data values, no data available, spurious unreliable data values, unknown fault or other).
Each elaborated data item comprises a Basic Data value.
MeasuredDataPublication¶
Objectives and utilisation mechanisms
This publication is used to give measured data which has been derived from equipment at specific measurement sites, where each site is identified by reference to an entry in a predefined measurement site table.
Content
This publication contains measurements from one or more sites.
With this publication, attributes can be given in the InformationHeader which provide clients with information management details (area of interest, confidentiality, information status, urgency) relating to this publication.
The measured data publication must contain a reference to the measurement site table used.
Each set of site measurement values must always contain a reference to the measurement site and a measurementTimeDefault which is the default time for each measured value if no other time is specified for an individual measurement.
Each set of site measurements has an ordered (indexed) list of measured values, where the order (index) corresponds with the measurement definition order (index) in the Measured Site table. So there is no need for any further identification for each measured value. The values that are measured are referenced by the index in the ordered list of values for that site.
A measured value can identify the type of measurement equipment used.
A measured value can also have a Location characteristics override. This is used to override the predefined lanes attribute and to indicate a reversal of flow compared with that was defined in the Measurement Site table.
In case of fault when measuring this data, it is possible to specify the type of fault (intermittent data values, no data available, spurious unreliable data values, unknown fault or other).
Each measured value comprises a Basic data value.
However the following points are of note for its use in the Measured Data publication:
- The point at which the measurement equipment is located (i.e. the site) is defined in the appropriate entry in the Measurement Site table. However, if the measurement relates to a section of road or a location (e.g. ANPR which determines measurements over a stretch of road) this can also be provided in the “pertinentLocation” which is an aggregation associated with the BasicData.
- TrafficStatus and TravelTimeData are normally provided as Elaborated data, but may be provided as Measured data if appropriate (e.g. because values are provided by an outstation).
Basic Data¶
Basic data value is a general abstract class which has the following attributes:
- Time precision, precision to which time of calculation or measurement is given
- Period (in seconds)
- Time, the time when basic data value was measured or elaborated.
Each Basic Data value can have a pertinent location. (see “location” paragraph). Generally, this location is identified by reference; see the paragraph concerning predefined locations.
Basic Data values are of one of the following types:
- Travel Time data
- Traffic Status
- Traffic data
- Weather data
The following paragraphs describe each of these basic data types:
Travel Time data
It has the following specific attributes:
- Travel time trend type: decreasing, increasing, stable
- Travel time type: best, estimated, instantaneous, reconstituted
- Vehicle type for this travel time.
It may be also associated with:
- Travel time (in seconds)
- Free flow travel time
- Normally expected travel time, as well as
- Free flow speed
Traffic Status
It has the following specific attribute:
- Traffic trend type: traffic building up, traffic easing, traffic stable, unknown.
and can be associated with
- Traffic status value: Impossible, congested, heavy, free flow, unknown if it differs from the reference value given for the publication
Traffic data
This value is usually sent as Measured Data, but may also be sent as Elaborated Data.
Traffic values can be classified on the basis of Vehicle characteristics.
There are 5 kinds of traffic values:
- Traffic headway
- Traffic flow
- Traffic speed
- Traffic concentration
- Individual vehicle measurements (not applicable for elaborated data).
Weather data
This value is (usually sent as Measured Data, but may also be sent as Elaborated Data).
There are 7 types of weather values:
- Precipitation information,
- Wind information,
- Temperature information,
- Pollution information,
- Road surface condition information,
- Visibility information,
- Humidity information.
However, the following point is of note for its use in the Elaborated Data publication:
- Traffic values and weather values are normally provided as Measured data, but may be provided as Elaborated data if appropriate (e.g. because values are provided by calculation).
MeasurementSiteTablePublication¶
Objectives and utilisation mechanisms
The Measurement Site Table publication is used to provide information relating to predefined measurement sites and the measurements that can be made at those sites. The sites and the details of their measurement characteristics are seen as static or quasi static (i.e. they seldom change).
The measurement site details and their measurement characteristics are referenced by Measured Data publications which enable these publications to be efficient when large volumes of measured data values need to be conveyed.
Content
This publication contains one or more measurement site tables.
With this publication, attributes can be given in the InformationHeader which provide clients with information management details (area of interest, confidentiality, information status, urgency) relating to this publication.
The Measurement Site table has a unique versioned identifier.
The Measurement Site table has a list of Measurement site records, each corresponding to a single measurement site. Every Measurement site record has a unique versioned identifier and the following attributes:
- Computation method,
- Measurement equipment reference,
- Measurement equipment type used,
- Measurement site name,
- Measurement site number of lanes,
- Measurement site identification,
- Measurement side,
- Measurement site record version and time.
The Measurement site record always has a single location.
Every site record must also have an ordered list of Measurement specific characteristics. This ordered (indexed) list of characteristics relates to the types of measurements that can be made at that measurement site. The ordering is significant because this order (indexing) is used in the Measured Data publications to distinguish between the different measurements received from the referenced site.
Measurement specific characteristics contains information about:
- Accuracy
- Period
- Smoothing factor
- Specific lane
- Specific measurement value type.
- Specific vehicle characteristics
These values are seen as static for the particular measurement at the site and do not have to be repeated for each measured value in the Measured data publication, unless they need to be overridden in particular cases (see Measured data publication section).
VMS¶
Warning
This publication in the version 3 PIM contentmodel is structured according to the version 2 content, mapped to the version 3 methodology, enabling the use of version 3 tooling. However: this publication is NOT an interoperable representation of the version 2 standard. The standard is in the process of revision according to CEN procedures and an update of this Publication is foreseen end of 2018.
VmsPublication¶
Objectives and utilisation mechanisms
This publication is used to give information on the current status and settings of one or more variable message signs (VMS) units, each unit controlling one or more individual variable message signs.
Content
This publication contains one or more VMS units.
With this publication, attributes can be given in the InformationHeader class which provide clients with information management details (area of interest, confidentiality, information status, urgency) relating to this publication.
Each VMS unit must always contain a reference to a versioned VMS Unit table and a reference to a versioned VMS unit record in this VMS Unit table which defines the characteristics of the VMS unit.
A VMS unit may control one or more variable message signs on a single gantry or on different gantries.
The VMS class provides the current status and settings of the VMS and the currently displayed information. Where a VMS is displaying a sequence or alternating set of messages these are ordered according to the messageIndex qualifier. Each VMS associated with a VMS unit is referenced by its vmsIndex. The vmsIndex also provides a reference to the specific VmsCharacteristics (defined in the VmsUnitTablePublication) that are relevant for the VMS which is controlled by the referenced VMS unit.
To assist in minimising the volume of required values to be sent for VMS messages covering wide expanses of a road network, characteristics of VMS and VMS units can be provided to a client using the VmsTablePublication.
In case of fault of VMS site or of VMS, it is possible to specify the type of fault (communication failure, power failure, out of service, incorrect message or pictogram display, unable to clear down, unknown fault or other).
A VMS is composed of:
- A general item if the VMS is working and about message sequencing interval in seconds, if applicable.
- The Text Display Area Settings (text lanterns, text luminance level, and luminance override).
- An ordered set of Pictogram Display Area Settings, one for each display area (picto lantern, picto luminance, …). Each pictogram display area on a VMS is referenced by its “pictogramDisplayAreaIndex” and details of its position relative to the text or its absolute position may be provided in VmsPictogramDisplayCharacteristics.
- An ordered set of VmsMessages. The messageIndex provides the ordering of a sequence of displayable messages. The VMS is displaying each message in turn according to its messageindex “order”. The sequence of messages displayed is continuously cycling.
In case a VMS is not defined previously in a VmsTablePublication, its static characteristics must be provided about:
- Its location in term of position (vmsLocation – practically defined with a point) and in term of managed logical location i.e. the road section (defined as a location reference) where the VMS is applicable.
- Its physical characteristics with VMS text display characteristics and VMS pictogram display characteristics. As a VMS may have several pictogram areas, every one is referenced by its pictogramDisplayAreaIndex. Every area may be completed by VMS supplementary panel characteristics.
These latter classes are defined more in details in the subsequent VMS table publication. Each elaborated data item comprises a Basic Data value.
Every VMS message comprises several elements. The adopted modelling takes into account different types of messages, with or without displayed text of several lines (in sequence), with or without pictogram display, each pictogram can have a VMS supplementary panel. The general information includes:
- VMS message information type (situation warning, travel time, traffic management, date and time, temperature, campaign message, instruction, future information).
- Time, the time when message was lst set
- Coded reason for setting (situation, campaign, operator created, traffic management, travel time or default) and the associated management or diversion plan.
- The authority, organisation or system which requested the setting of the message and the one which set it.
- References towards the related situations and situation records for which the message is related.
- Distance of the VMS from the location of the related situation record/element
A VMS message includes:
- One or several text pages. Where multiple pages of text are defined each is referenced by its “pageNumber” and is displayed sequentially according to the “pageNumber” order in the same display area.
- Each VMS text page comprises one or several lines of text. Where multiple lines of text are defined each is referenced by its “lineIndex” qualifier and is ordered accordingly. The VMS text line is also defined by the text itself, its colour, the used language, if it is flashing or not.
- One or several VMS pictogram display areas. Each pictogram display area on a VMS is referenced by its “pictogramDisplayAreaIndex” and details of its position relative to the text or its absolute position may be provided in VmsPictogramDisplayCharacteristics.
- Each VMS pictogram display area may display one pictogram or a sequence of pictograms. The order of sequencing of the pictograms is defined by the “pictogramSequenceIndex” values.
- Each VMS pictogram can be defined by one or several pictogram description, a code, the value of distance,, length, weight or width to be displayed on the pictogram, if the pictogram is in inverse colour or if there is presence or red triangle or not, if it is compliant with the Vienna convention on road signs and signals, …
- A pictogram can be supplemented by one VMS supplementary panel which consists in one VMS text line (see above for description)
VmsTablePublication¶
Objectives and utilisation mechanisms
The VMS Table publication is a publication containing one or more VMS Unit Tables each comprising a set of records which hold details of VMS units. The VMS sites and the details of their characteristics are seen as static or quasi static (i.e. they seldom change).
The VMS tables and their VMS unit characteristics are referenced by VMS publications which enable these publications to be efficient when large volumes of displayed messages need to be conveyed.
Content
This publication contains one or more VMS unit tables.
With this publication, attributes can be given in the InformationHeader which provide clients with information management details (area of interest, confidentiality, information status, urgency) relating to this publication.
The VMS unit table has a unique versioned identifier.
The VMS unit table has a list of VMS unit records, each corresponding to a single VMS unit (entity managing one or several physical VMSs).
Every VMS unit record has a unique versioned identifier and the following attributes:
- Number of VMS,
- VMS unit identifier,
- VMS unit electronic address,
- VMS unit IP address,
Every VMS unit record must also have an ordered list of VMS records containing the physical characteristics and the location of each VMS. This ordered (indexed) list of these characteristics relates to different display areas on the VMS. The ordering is significant because this order (indexing) is used in the VMS publications to distinguish between the different display areas.
The VMS record can have until two location references. The first one gives the physical VMS location in term of position (vmsLocation – practically defined with a point) location references and the second one gives its managed logical location i.e. the road section (defined as a location reference – practically defined with one or several linears) where the VMS is applicable.
The VMS record also contains global information about:
- VMS type (colour graphic, monochrome graphic, continuous sign, matrix sign, other)
- Number of pictogram display areas
- VMS description
- VMS display height and width, its height above roadway
- VMS physical mounting (gantry, central reservation, roadside and roadside cantilever, overhead bridge, tunnel entrance, trailer and vehicle)
- VMS owner
- VMS type code.
- If its display areas are dynamically configurable.
It can also contain information for the VMS text display characteristics:
- Maximum font height, width and spacing
- Maximum numbers of characters, rows and sequential pages
- Maximum text luminance level
- Minimum font height, width and spacing
- Text display height and width
- Text lanterns presence
- Text page sequencing capability
- Number of text pixels across and down
- Text position absolute (on left, on right, at top, at bottom) and coordinates (X & Y) in metres
- Legend code list identifier
As well as for each VMS pictogram display characteristics through its “pictogramDisplayAreaIndex”, details of its position relative to the text or its absolute position may be provided like:
- Maximum number of sequential pictograms
- Pictogram display height and width
- Pictogram number of colours
- Maximum pictogram luminance level
- Pictogram lanterns presence
- Pictogram sequencing capability
- Number of pictogram pixels across and down
- Pictogram position absolute (on left, on right, at top, at bottom), relative to text (above, below, to the left, to the right) and coordinates (X & Y) in metres
- Pictogram code list identifier
These values are seen as static for the particular VMS and do not have to be repeated for each displayed message in the VMS publication, unless they need to be overridden in particular cases (see VMS publication section).