Traffic speed
DATEX II packages addressed by the RRP The types of data on the real-time use of the network
This RRP tailors the following DATEX II model packages:
- Common – commonly used DATEX II data elements used by the tailored packages below (CEN/EN 16157-7:2018)
- LocationReferencing – the location references, tailored for traffic speed data (CEN/EN 161578-2: 2019)
- RoadTrafficData – the DATEX II package for sensor data, tailored for traffic speed data (CEN/EN 16157-5:2020)
The RoadTrafficData is used for publishing sensor data information on traffic speed.
It shall be uses as:
- an ElaboratedDataPublication, for simple traveltime data provision.
ElaboratedData profile
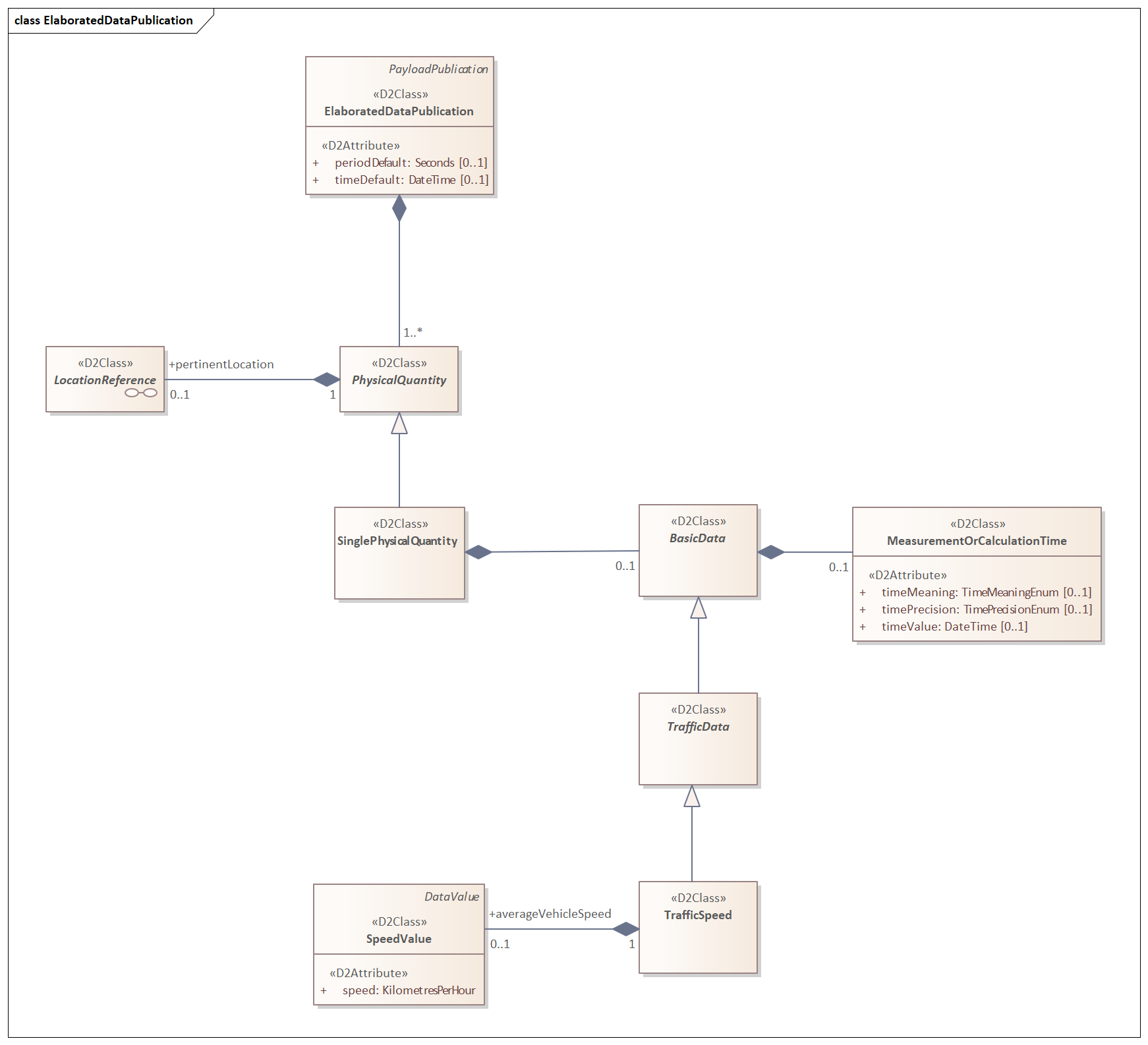
The RoadTrafficData package is used to provide sensor measurements in ElaboratedDataPublication as a PhysicalQuantity -> SinglePhysicalQuantity specialising as TrafficData -> TrafficSpeed, having averageVehicleSpeed
Instances of ElaboratedDataPublication contain one or more PhysicalQuantities (one per measurement per pertinentlocation), see Figure 1.
Figure 1 PhysicalQuantity in an elaborated data publication
This RRP uses the following attribute:
- speed
LocationReference profile
This RRP does not specify the locationreferencing methods to use. The applied method for location referencing is the choice of the specific user implementing this profile. The location of a measurement site for traffic speed could either be a point, or a linear section of road.
This RRP does limit the use of SupplementaryPositionalDescription to identifying the affected carriageways and lanes on which the provided traffic speed is valid.
Where relevant the lane identification and its use is provided as specificLane in the supplementaryPositionalDescription of the location.
laneUsage and laneNumber shall be used jointly to characterise lanes that are affected.
Application of the RRP
The RRP can be selected in the schema creation wizard at DATEX II webtool.
- If you want to implement the RRP “as-is”, you simply click through the wizard starting with the default selection of the package in the first step.
You skip Step 2
Choose the respective RRP in Step 3.
In step 4 you select the locationreferencing method you are going to implement.
Then you skip the subsequent steps and choose which type of output (XML Schema or JSON Schema) you want to produce in Step 6.
These schemas will then be used by the implementer of you RRP to create the interface software, e.g. by application of data binding.
If you service manages more data elements which have not been selected in the RRP, it is possible to extend the profile in Step 5 by selecting further elements.